28 Beautiful Begonia Rex Varieties With Pictures
Written by Ivy
Dec 30 2021

Begonia rex has stout and hypertrophic rhizomes, fleshy, creeping and very short nodes. Both leaves and flower stems grow from the rhizome node and grow into a cluster near the ground. The leaves are obliquely ovate, dark green on the leaf surface, often with metallic luster, irregular silver white ring, red on the back of the leaves, hairy veins and petioles. There are many varieties of Begonia rex horticulture, mainly due to different leaf color and markings. The leaves of Begonia rex are very beautiful and are the main ornamental parts. Begonia rex is an important shade loving potted foliage plant and greenhouse potted flower. Begonia rex is widely cultivated and loved by people all over the world. Next, I will list 28 very beautiful Begonia rex variations.
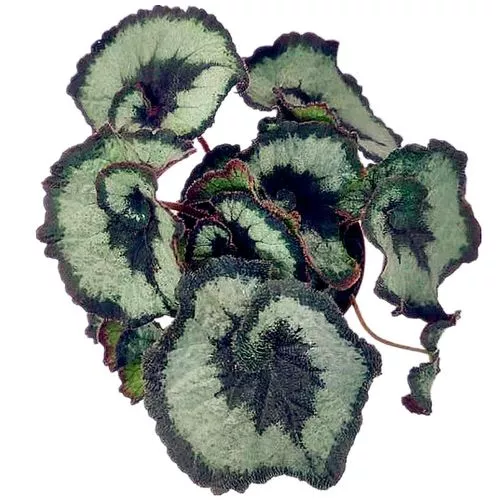
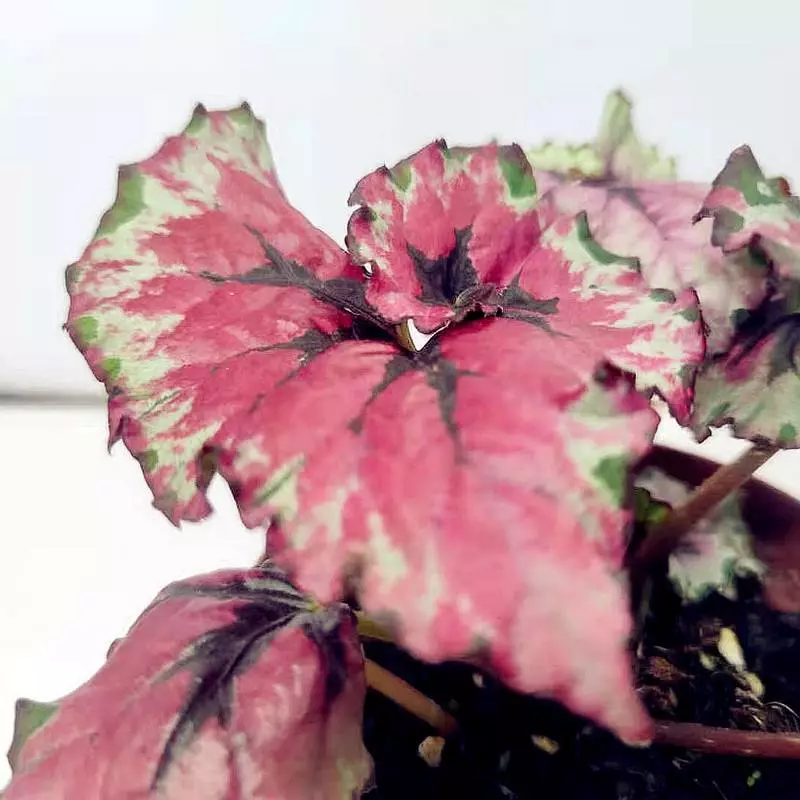
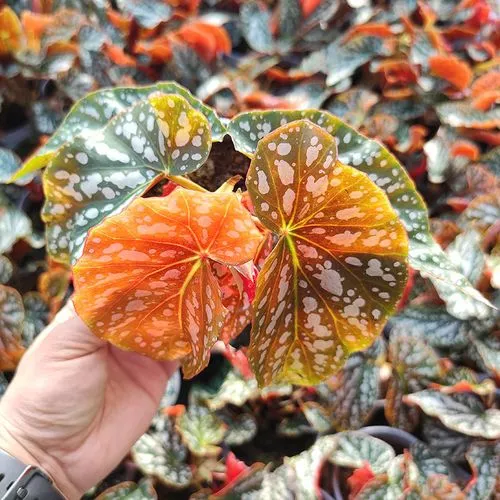
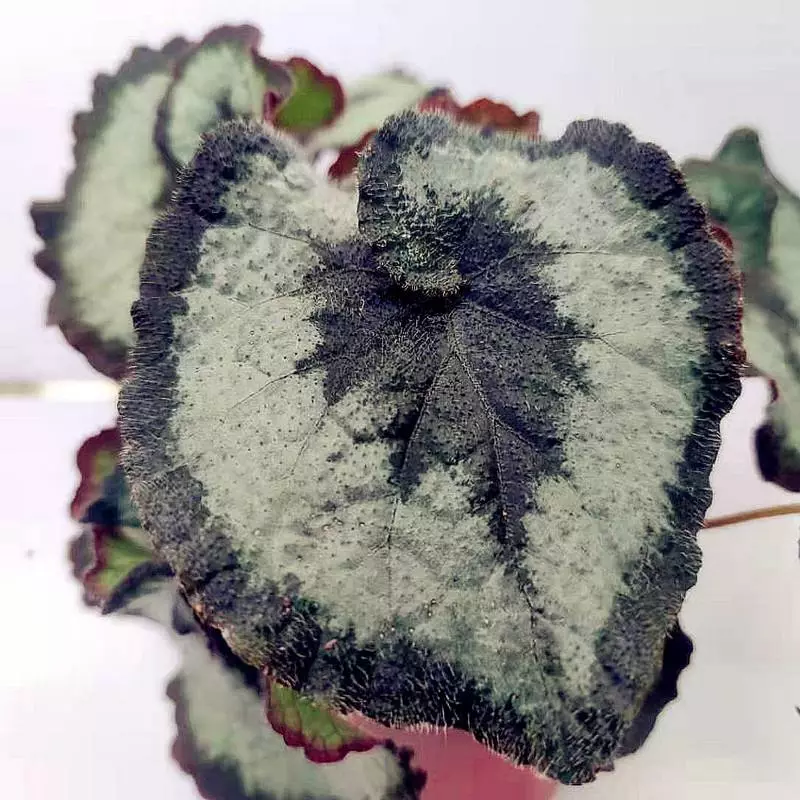
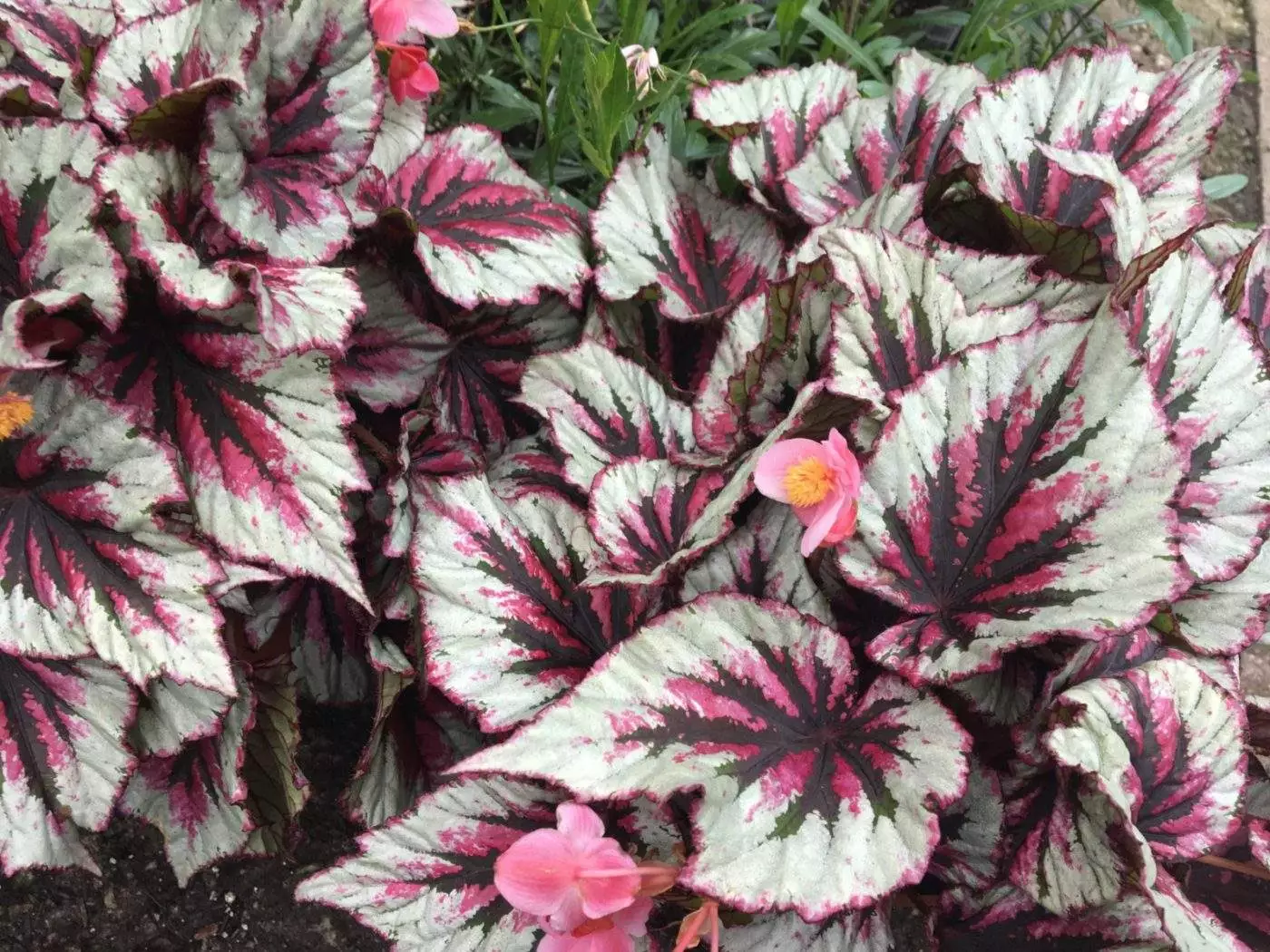
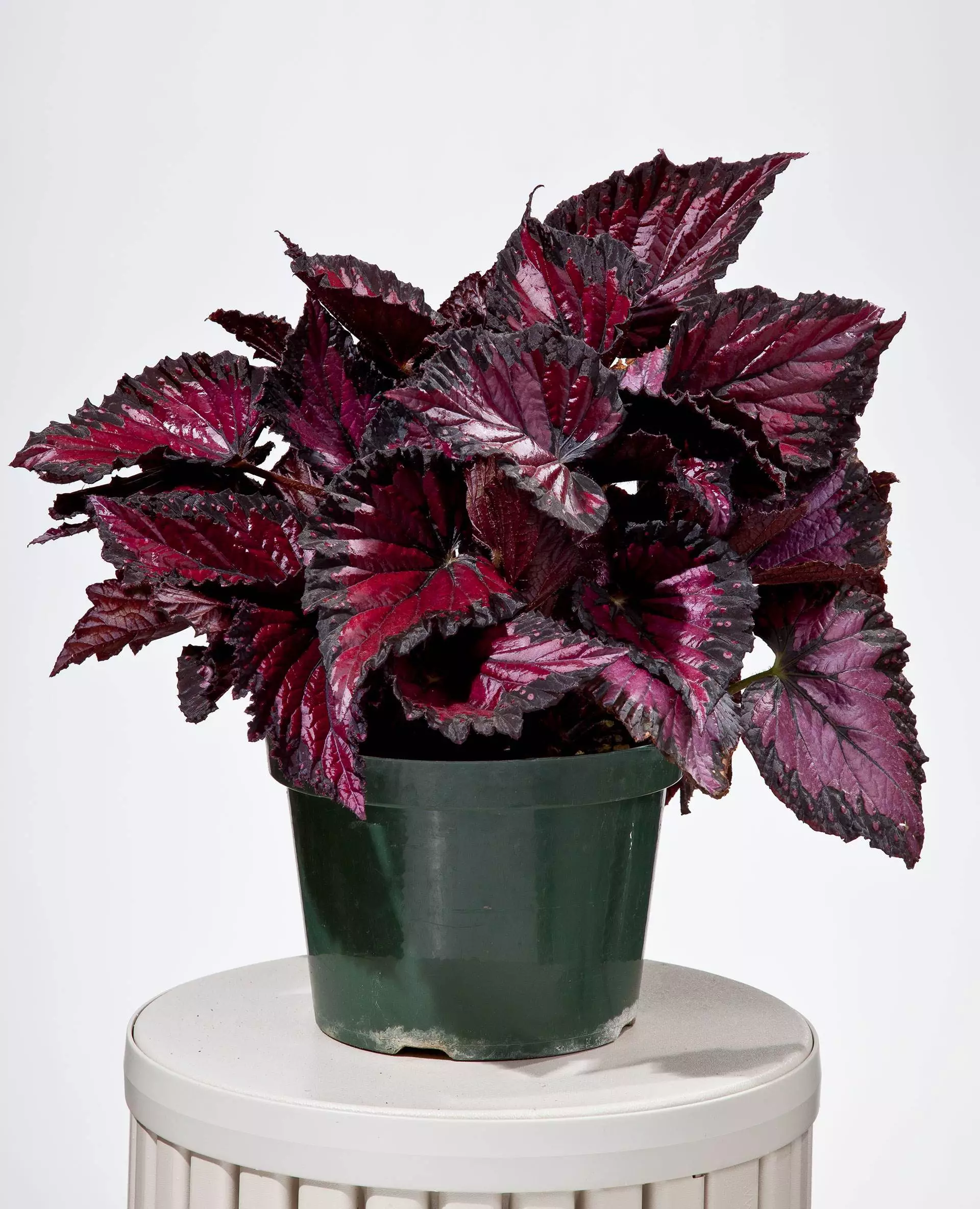
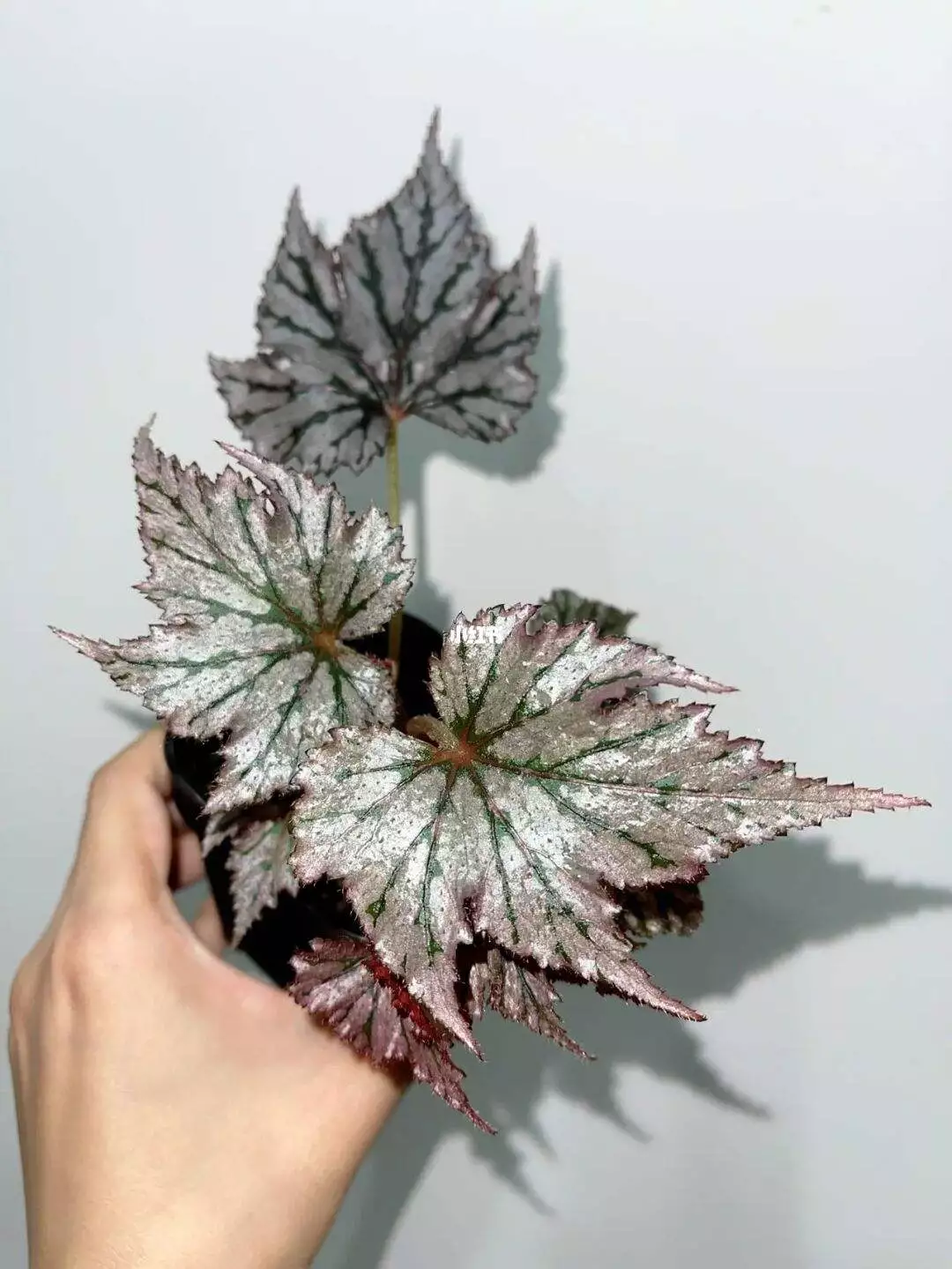
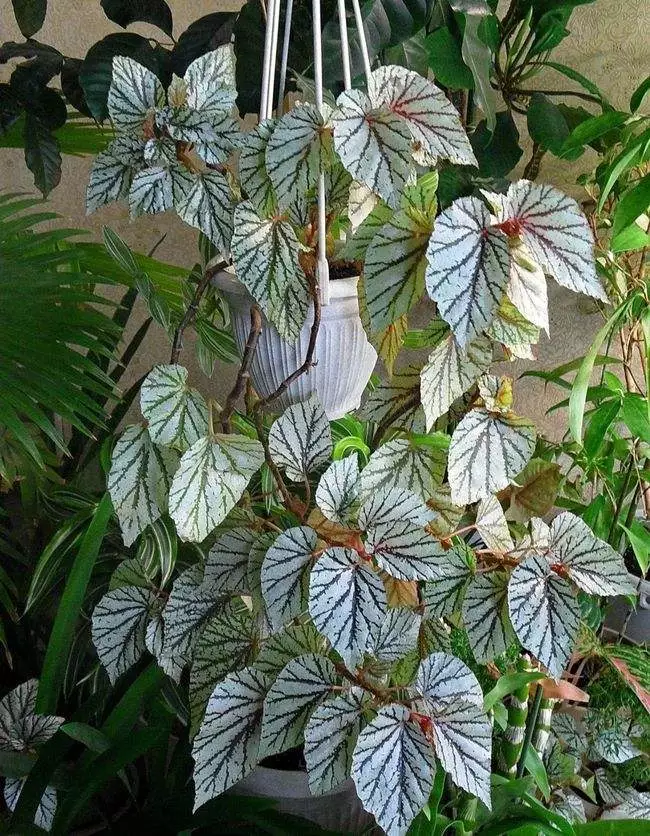
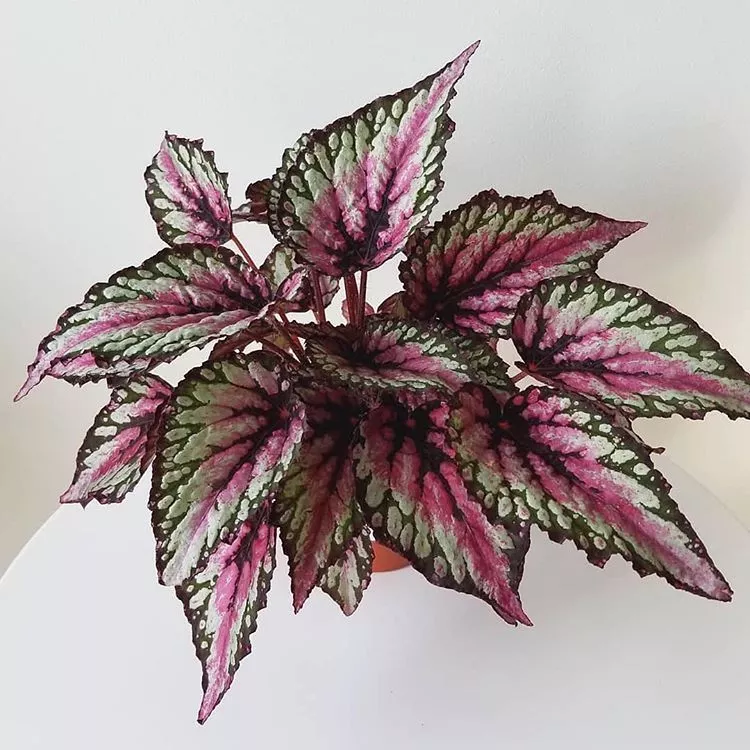
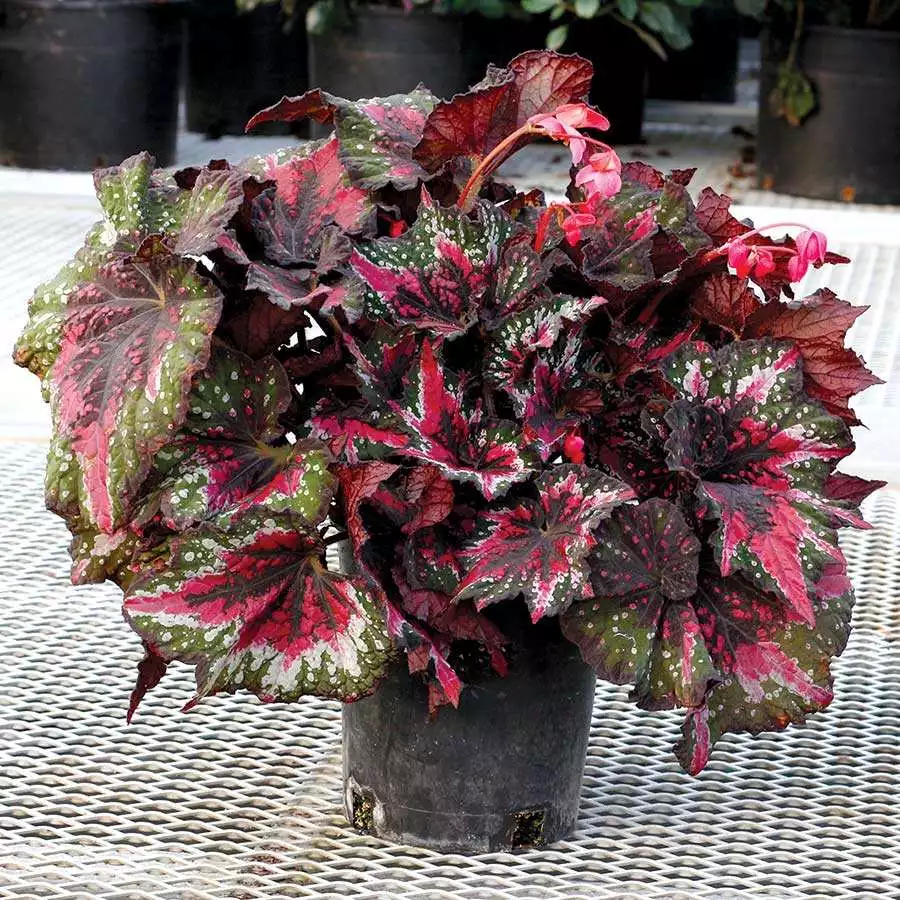
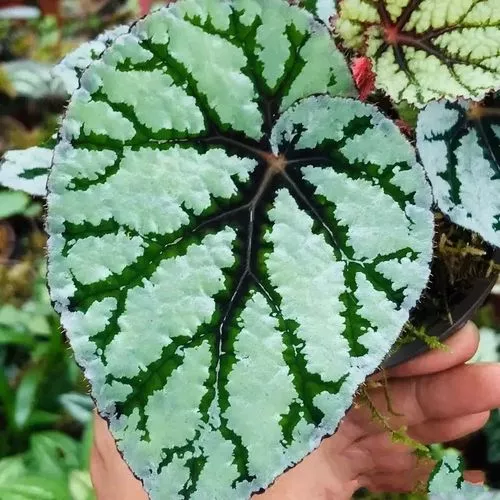
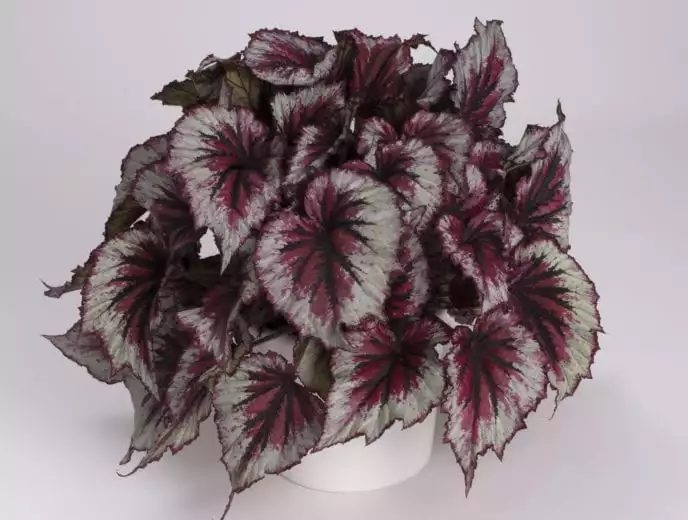
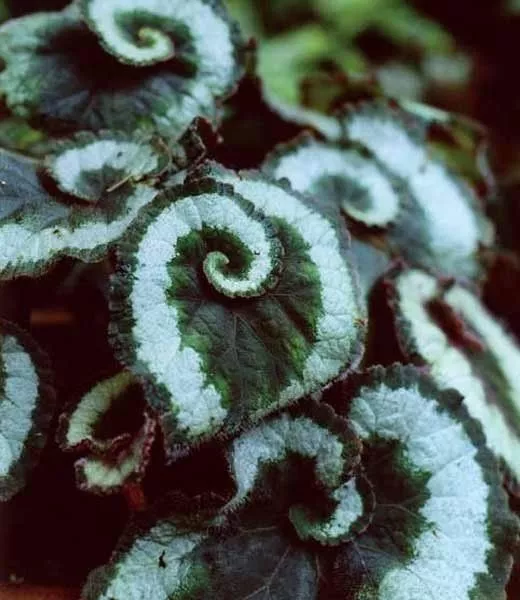
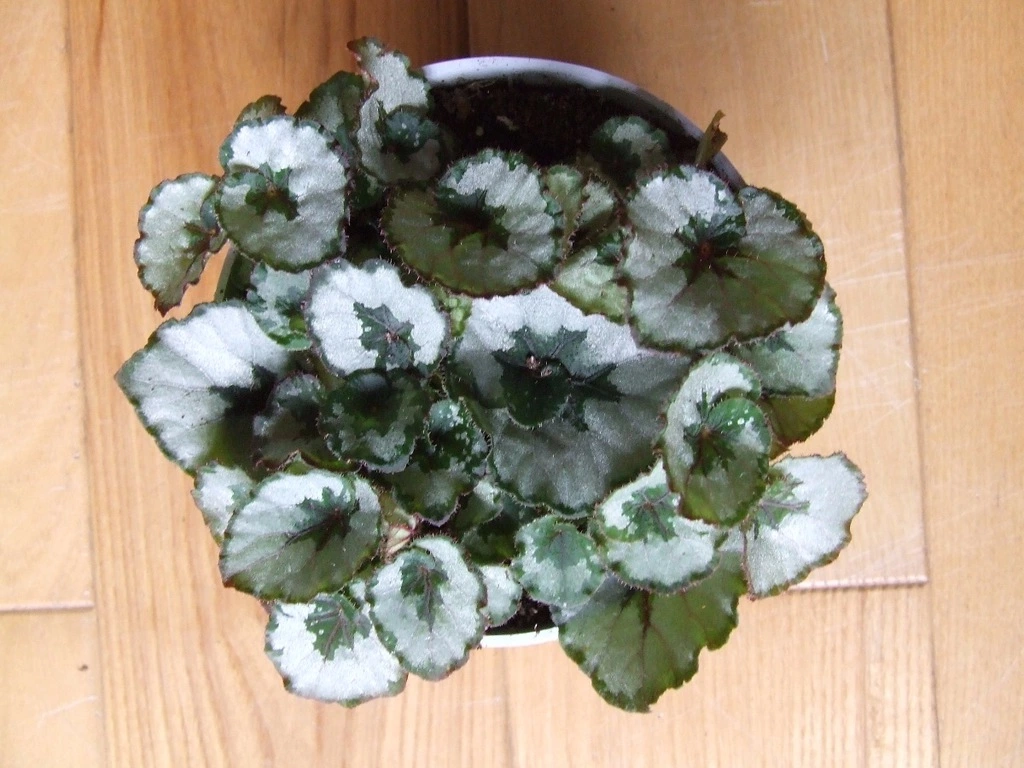
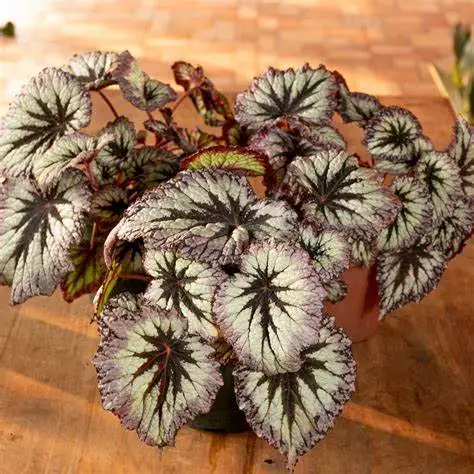
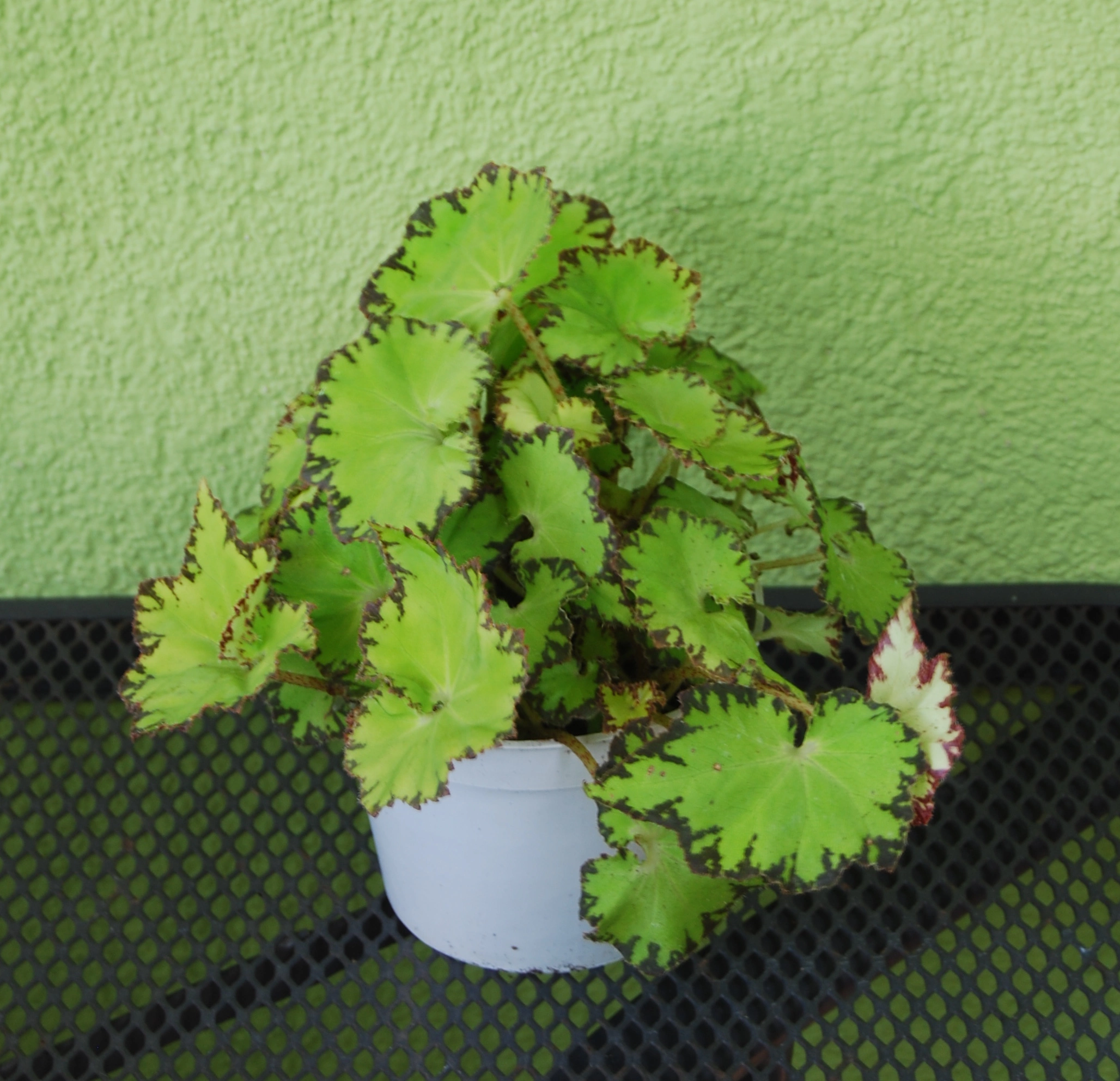
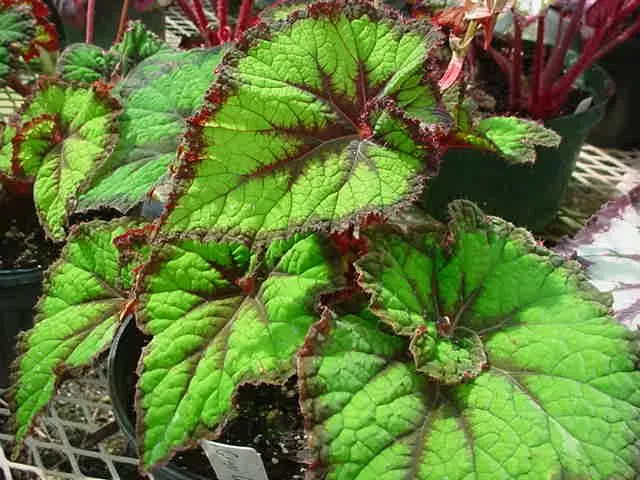
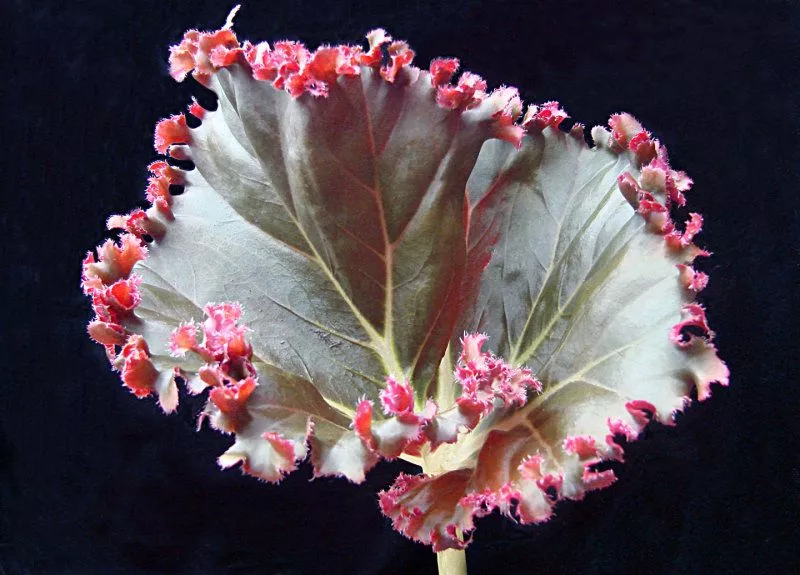
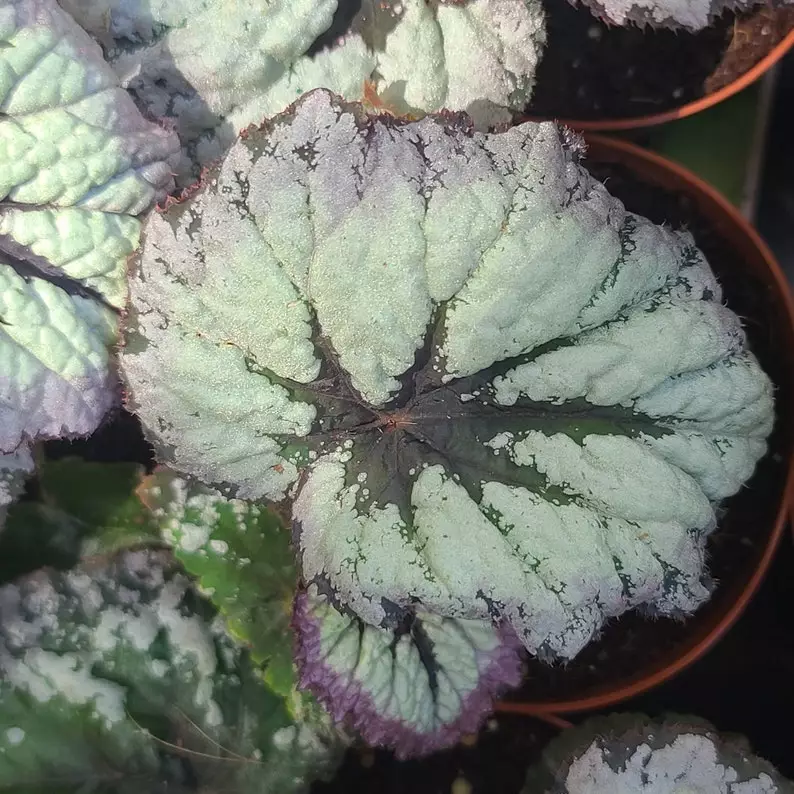























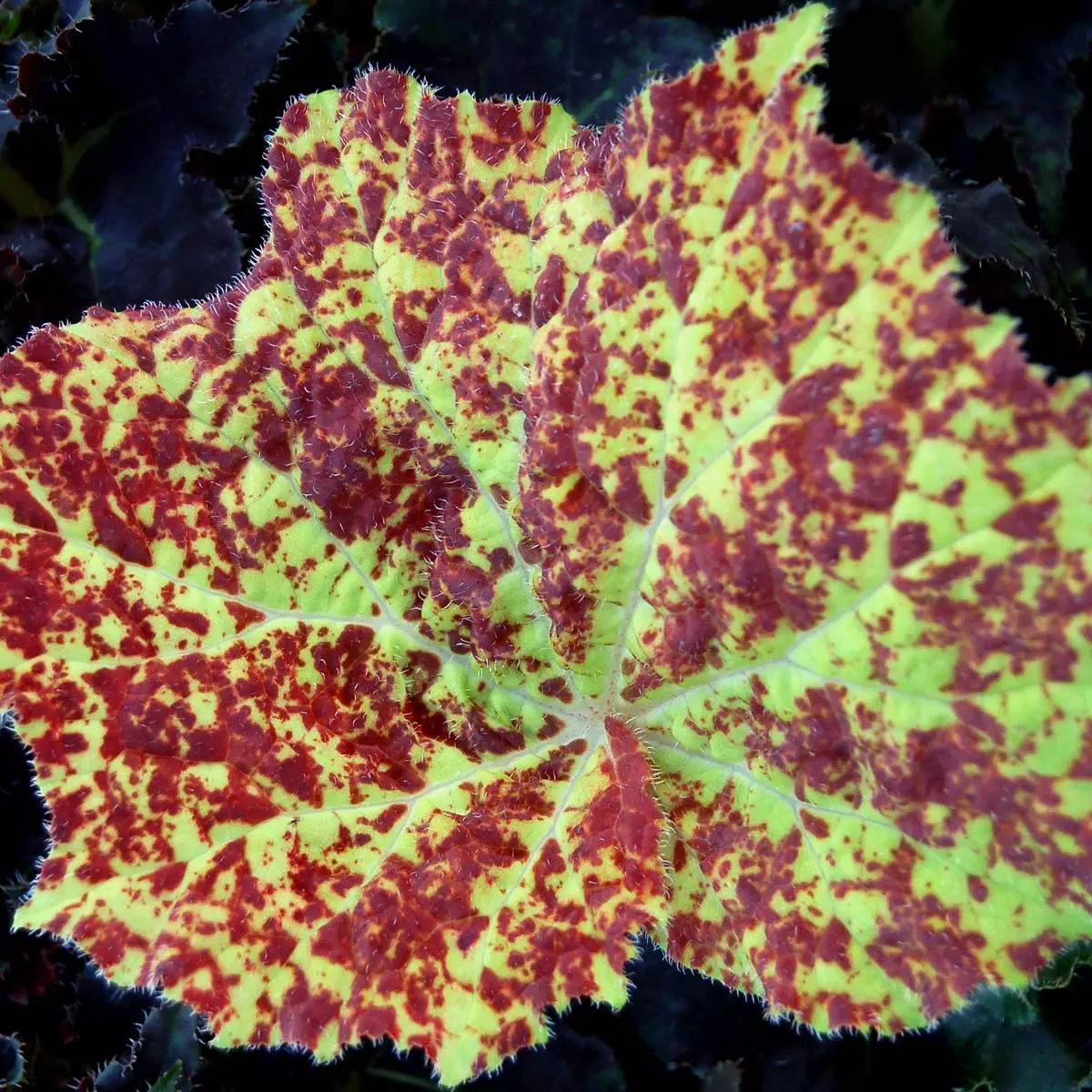




Begonia Rex is produced in warm and humid tropical forests, often in rock crevices and other places where the soil layer is shallow but contains more humus. Special attention should be paid to shading during culture. For cultivation in greenhouse, the shading should be about 70% in summer, 50% in spring and autumn and 30% in winter. It is necessary to maintain high air humidity in all seasons. We can spray water around Begonia rex several times a day, and a small amount of water can also be sprayed on the leaves in dry spring. If the air humidity is too low or the sun is too strong, the leaves will roll back, and dead patches will appear on the edge or leaf surface.
Begonia Rex potting soil is made of rotten leaf soil or peat soil, 1 / 3 of river sand and some rotten cow dung and chicken dung as base fertilizer. Potting should not be too deep. It is better to have the rhizome flush with the surface of the basin soil. Begonia rex can change pots every spring to remove the old soil and rotten roots and replant them with new soil.
Begonia Rex is not cold resistant. In winter, the room temperature should be above 12 ℃, and the appropriate temperature is 18 ~ 25 ℃. The high temperature and dry environment is very unfavorable to the growth of Begonia rex, which often makes the leaves small and thick. In serious cases, the edge of the leaves is dry, and the young leaves cannot expand until they die. High temperature and humidity are also easy to cause plant decay. In rainy and high-temperature dog days, we should move Begonia rex to a rain sheltered, ventilated and cool place.
FairyRumbaPink CharmingTornadoAngel WingDuartenBallet RexRed Kiss RexSilver LimboYamilethSalsaSpitfireFlamencoHarmony Black BeautyCeliaBlueberry SorbetChampagne BubblesChristmas CurlFireworksRiver NileGreen GoldCowardly LionEscargotMarmadukeStained GlassNorthern LightsMadame QueenPlum PaisleyBegonia Rex Care Methods
Fairy

Rumba

Pink Charming

Tornado

Angel Wing

Duarten

Ballet Rex

Red Kiss Rex

Silver Limbo

Yamileth

Salsa

Spitfire

Flamenco

Harmony Black Beauty

Celia

Blueberry Sorbet

Champagne Bubbles

Christmas Curl

Fireworks

River Nile

Green Gold

Cowardly Lion

Escargot

Marmaduke

Stained Glass

Northern Lights

Madame Queen

Plum Paisley

Begonia Rex Care Methods
We usually uses division, leaf cutting and sowing propagation to plant Begonia Rex. Begonia Rex propagation by division should be carried out in spring. The rhizome should be divided into two or more segments, so that each segment has at least new buds and 2 ~ 3 leaves. After the wound is slightly dried, plant it into the basin respectively. The depth is better if the upper part of the rhizome is flush with the soil surface or 1 cm below the soil surface. Leaf cutting can be carried out in the whole growing season, preferably in March ~ June or August ~ October in the family. At present, most of the cultivated begonia rex are excellent varieties, which are clones selected through hybridization. In general, most of the Begonia rex seedlings tend to be wild species. Sowing is only used to breed new varieties.Begonia Rex is produced in warm and humid tropical forests, often in rock crevices and other places where the soil layer is shallow but contains more humus. Special attention should be paid to shading during culture. For cultivation in greenhouse, the shading should be about 70% in summer, 50% in spring and autumn and 30% in winter. It is necessary to maintain high air humidity in all seasons. We can spray water around Begonia rex several times a day, and a small amount of water can also be sprayed on the leaves in dry spring. If the air humidity is too low or the sun is too strong, the leaves will roll back, and dead patches will appear on the edge or leaf surface.
Begonia Rex potting soil is made of rotten leaf soil or peat soil, 1 / 3 of river sand and some rotten cow dung and chicken dung as base fertilizer. Potting should not be too deep. It is better to have the rhizome flush with the surface of the basin soil. Begonia rex can change pots every spring to remove the old soil and rotten roots and replant them with new soil.
Begonia Rex is not cold resistant. In winter, the room temperature should be above 12 ℃, and the appropriate temperature is 18 ~ 25 ℃. The high temperature and dry environment is very unfavorable to the growth of Begonia rex, which often makes the leaves small and thick. In serious cases, the edge of the leaves is dry, and the young leaves cannot expand until they die. High temperature and humidity are also easy to cause plant decay. In rainy and high-temperature dog days, we should move Begonia rex to a rain sheltered, ventilated and cool place.
Latest Updated
- Benefits of Bugleweed - 7 Science-backed Health Benefits
- Bugleweed Dangers & Side Effects - Is It Poisonous?
- How to Plant Evergreen Trees - What You Should Know
- When to Plant Evergreens - Grow Guide for Evergreen Trees
- 12 Wonderful Evergreen Shrubs for Your Garden
- 12 Popular Evergreen Plants with Pictures for Beginners
- When And How To Prune A Lilac Bush Like a Pro
- How to Grow & Care for Lilac Vine (Hardenbergia Violacea)
- Japanese Lilac Tree (Syringa Reticulata) Care & Propagation Guide
- Shumard Oak Pros and Cons - What to Know
Popular Articles
- Winter maintenance of Antirrhinum Majus
- How to Grow Terminalia Mantaly Tree
- How to Grow and Care for Crossostephium Chinense
- How to grow Antirrhinum Majus in spring
- Peristeria Elata (Dove Orchid) Profile: Info & Care Guide
- Underwatered Snake Plant (Sansevieria Trifasciata) - Signs And How To Fix
- How to Care for Brazilian Jasmine Plant (Mandevilla Sanderi)
- How to Grow & Care for Graptopetalum Purple Delight in Summer
- Rosa Chinensis (China Rose): Plant Growing & Care Tips
- How to Care for Baby Sun Rose (Aptenia Cordifolia)